Abstract
Research Article
Reasons why new coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2 infections are likely to spread
Takuma Hayashi*, Takashi Ura, Kaoru Abiko, Masaki Mandan, Nobuo Yaegashi and Ikuo Konishi
Published: 28 April, 2020 | Volume 3 - Issue 1 | Pages: 001-003
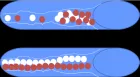
The ongoing outbreak of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) originally emerged in China during December 2019 and had become a global pandemic by March 2020. COVID-19 is caused by a novel coronavirus, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus type 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Two other coronaviruses have caused world-wide outbreaks in the past two decades, namely SARS-CoV (2002–2003) and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) (2012–present). The surface spike glycoprotein (S), which is critical for virus entry through engaging the host receptor and mediating virus host membrane fusion, is the major antigen of coronaviruses. Recent studies provide molecular insights into antibody recognition of SARS-CoV-2. In this review, we discuss the relationship between the spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 and its receptor, angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) including the latest findings.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.jgmgt.1001005 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
ACE2; Furin; SARS-CoV-2; COVID-19; SARS-CoV
References
- Coronavirus disease (COVID-2019) situation reports. Geneva: World Health Organization. 2020. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situation-reports/
- Zhou P, Yang XL, Wang XG, Hu B, Zhang L, et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature. 2020; 579: 270-273. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32015507
- Wrapp D, Wang N, Corbett KS, Goldsmith JA, Hsieh CL, et al. Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation. Science. 2020; 367: 1260-1263. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32075877
- Andersen KG, Rambaut A, Lipkin WI, Edward C, Holmes EC, et al. The proximal origin of SARS-CoV-2. Nature Medicine. 2020; 26: 450–452.
- Pesu M, Watford WT, Wei L, Xu L, Fuss I, et al. T-cell-expressed proprotein convertase furin is essential for maintenance of peripheral immune tolerance. Nature. 2008; 455: 246-250. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18701887
- Ji HL, Zhao R, Matalon S, Matthay MA. Elevated Plasmin(ogen) as a Common Risk Factor for COVID-19 Susceptibility. Physiol Rev. 2020; 100: 1065-1075. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32216698
- Walls AC, Park YJ, Tortorici MA, Wall A, McGuire AT, et al. Structure, Function, and Antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein. Cell. 2020: 181: 281-292. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32155444
- Abraham S, Kienzle TE, Lapps W, Brian DA. Deduced sequence of the bovine coronavirus spike protein and identification of the internal proteolytic cleavage site. Virology. 1990; 176: 296-301. PubMed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2184576
- Shi J, Wen Z, Zhong G, Yang H, Wang C, et al. Susceptibility of ferrets, cats, dogs, and other domesticated animals to SARS–coronavirus 2. Science. 2020; pii: eabb7015. Pubmed: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32269068
- Lewis d. Is the coronavirus airborne? Experts can’t agree. Nature. 2020.
Figures:
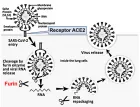
Figure 1
Figure 2

Figure 3
Similar Articles
-
Reasons why new coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2 infections are likely to spreadTakuma Hayashi*,Takashi Ura,Kaoru Abiko,Masaki Mandan,Nobuo Yaegashi,Ikuo Konishi. Reasons why new coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2 infections are likely to spread. . 2020 doi: 10.29328/journal.jgmgt.1001005; 3: 001-003
Recently Viewed
-
CT-guided Retrograde Urography as a Diagnostic Tool for Post-kidney Transplantation Evaluation: A Case ReportHan-Mei Chang, Chan-I Su, Ching-Ting Chang*. CT-guided Retrograde Urography as a Diagnostic Tool for Post-kidney Transplantation Evaluation: A Case Report. J Clin Med Exp Images. 2023: doi: 10.29328/journal.jcmei.1001028; 7: 004-006
-
Dual Role of Clinician Managers in Healthcare - Challenges and OpportunitiesAhsana Nazish*. Dual Role of Clinician Managers in Healthcare - Challenges and Opportunities. J Clin Med Exp Images. 2023: doi: 10.29328/journal.jcmei.1001029; 7: 007-013
-
Pancreatico-gastric FistulaRony Varghese*, Amal Upadhyay, Pawan Kumar Jaiprakah Maniyar. Pancreatico-gastric Fistula. J Clin Med Exp Images. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jcmei.1001030; 8: 001-002
-
A Rare Consanguineous Case of Alazami Syndrome in a Jordanian Family: Clinical Presentation, Genetic Analysis, and Therapeutic Approaches - A Case ReportFawzi Irshaid*, Salim Alawneh, Qasim Al Souhail, Aisha Alshdefat, Bashar Irshaid, Ahmed Irshaid. A Rare Consanguineous Case of Alazami Syndrome in a Jordanian Family: Clinical Presentation, Genetic Analysis, and Therapeutic Approaches - A Case Report. J Clin Med Exp Images. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jcmei.1001031; 8: 003-006
-
Establishment of a Best Practice Recommendation (BPR) for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms in a Large Multi-State Radiology Practice: Adoption and ImpactAndrew K Hillman, Phil Ramis, Patrick Nielsen, Eric M Rohren*. Establishment of a Best Practice Recommendation (BPR) for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms in a Large Multi-State Radiology Practice: Adoption and Impact. J Clin Med Exp Images. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jcmei.1001032; 8: 007-012
Most Viewed
-
Causal Link between Human Blood Metabolites and Asthma: An Investigation Using Mendelian RandomizationYong-Qing Zhu, Xiao-Yan Meng, Jing-Hua Yang*. Causal Link between Human Blood Metabolites and Asthma: An Investigation Using Mendelian Randomization. Arch Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.aaai.1001032; 7: 012-022
-
Impact of Latex Sensitization on Asthma and Rhinitis Progression: A Study at Abidjan-Cocody University Hospital - Côte d’Ivoire (Progression of Asthma and Rhinitis related to Latex Sensitization)Dasse Sery Romuald*, KL Siransy, N Koffi, RO Yeboah, EK Nguessan, HA Adou, VP Goran-Kouacou, AU Assi, JY Seri, S Moussa, D Oura, CL Memel, H Koya, E Atoukoula. Impact of Latex Sensitization on Asthma and Rhinitis Progression: A Study at Abidjan-Cocody University Hospital - Côte d’Ivoire (Progression of Asthma and Rhinitis related to Latex Sensitization). Arch Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.aaai.1001035; 8: 007-012
-
An algorithm to safely manage oral food challenge in an office-based setting for children with multiple food allergiesNathalie Cottel,Aïcha Dieme,Véronique Orcel,Yannick Chantran,Mélisande Bourgoin-Heck,Jocelyne Just. An algorithm to safely manage oral food challenge in an office-based setting for children with multiple food allergies. Arch Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.aaai.1001027; 5: 030-037
-
Snow white: an allergic girl?Oreste Vittore Brenna*. Snow white: an allergic girl?. Arch Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.aaai.1001029; 6: 001-002
-
Cytokine intoxication as a model of cell apoptosis and predict of schizophrenia - like affective disordersElena Viktorovna Drozdova*. Cytokine intoxication as a model of cell apoptosis and predict of schizophrenia - like affective disorders. Arch Asthma Allergy Immunol. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.aaai.1001028; 5: 038-040

If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."